What is Statics?
| Branch of physical sciences concerned with the
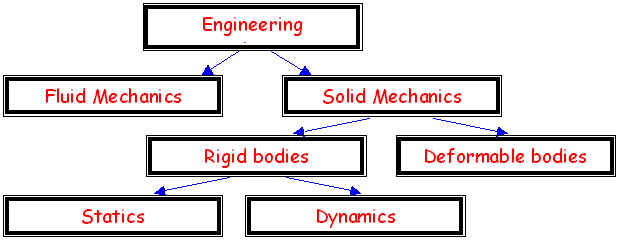
state of rest or motion of bodies subjected to forces is called Mechanics. The following diagram shows that Statics stands under solid mechanics of rigid bodies.
|
 |
Course objective
By the end of this course, you should be able to:
| Determine the components of a force in rectangular or nonrectangular coordinates. | |
| Determine the resultant of a system of forces. | |
| Draw complete and correct free-body diagrams and write the appropriate equilibrium equations from the free-body diagram. | |
| Determine the support reactions on a structure. | |
| Determine the connection forces in trusses and in general frame structures. | |
| Determine the internal reactions in a beam, draw correct shear-force and bending moment diagrams, and write equations for the shear-force and bending moment as functions of position along the beam. | |
| Analyze systems that include frictional forces. | |
| Locate the centroid of an area. | |
| Calculate the second moment of an area, calculate the principal second moments of an area. |
The suggested textbooks are:
| Engineering Mechanics: Statics. 2nd Edition, by W.F. Riley and L.D. Sturges. Published by John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York. 1996. | |
| Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics, Sixth Edition, by F. P. Beer and E. R. Johnson, published by McGraw-Hill. | |
| Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 9e, Hibbeler, 2001, Prentice Hall. |

